Vitamin B12 is one of the most essential vitamins for your body, playing a vital role in energy production, red blood cell formation, and nervous system function. Yet, B12 deficiency is increasingly common, especially in India, and its long-term consequences can be serious and irreversible.
In this post, we’ll explore the causes of B12 deficiency, the challenges with absorption, and practical solutions to ensure you maintain healthy B12 levels.
Why Is Vitamin B12 So Important? #
Vitamin B12 (also known as cobalamin) is essential for:
- Red blood cell production: Prevents anemia and maintains energy.
- Nervous system health: Supports brain function and nerve repair.
- DNA synthesis: Essential for cell division and growth.
A deficiency in B12 can lead to fatigue, brain fog, nerve damage, and other severe health issues.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency #
B12 deficiency occurs due to two main reasons:
- Not Consuming Enough B12-Rich Foods
- Vitamin B12 is only found in animal-based foods like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy.
- Vegetarians and vegans are particularly at risk because their diet lacks natural sources of B12.
✅ Important Note: Eggs and dairy are considered inferior sources of B12 because they have low bioavailability, meaning the body absorbs very little of the B12 they contain.
- Poor Absorption in the Gut
Even if you eat B12-rich foods, your body may not absorb it effectively due to:- Low stomach acid: Stomach acid is essential for breaking down food and releasing B12.
- Lack of intrinsic factor: Intrinsic factor is an enzyme produced in the stomach that binds to B12 and helps your body absorb it.
- Gut issues: Long-term use of medications like antacids and PPIs (proton pump inhibitors) can damage gut health, reducing B12 absorption.
Why Is B12 Deficiency Common in India? #
In India, B12 deficiency is often a combination of both factors:
- A diet low in B12-rich foods due to cultural preferences for vegetarianism.
- Widespread gut issues caused by poor eating habits, medication abuse, and low stomach acid.
Many people rely on fortified foods (like cereals or milk with added B12), but these often come with other problems, such as added sugar or artificial additives.
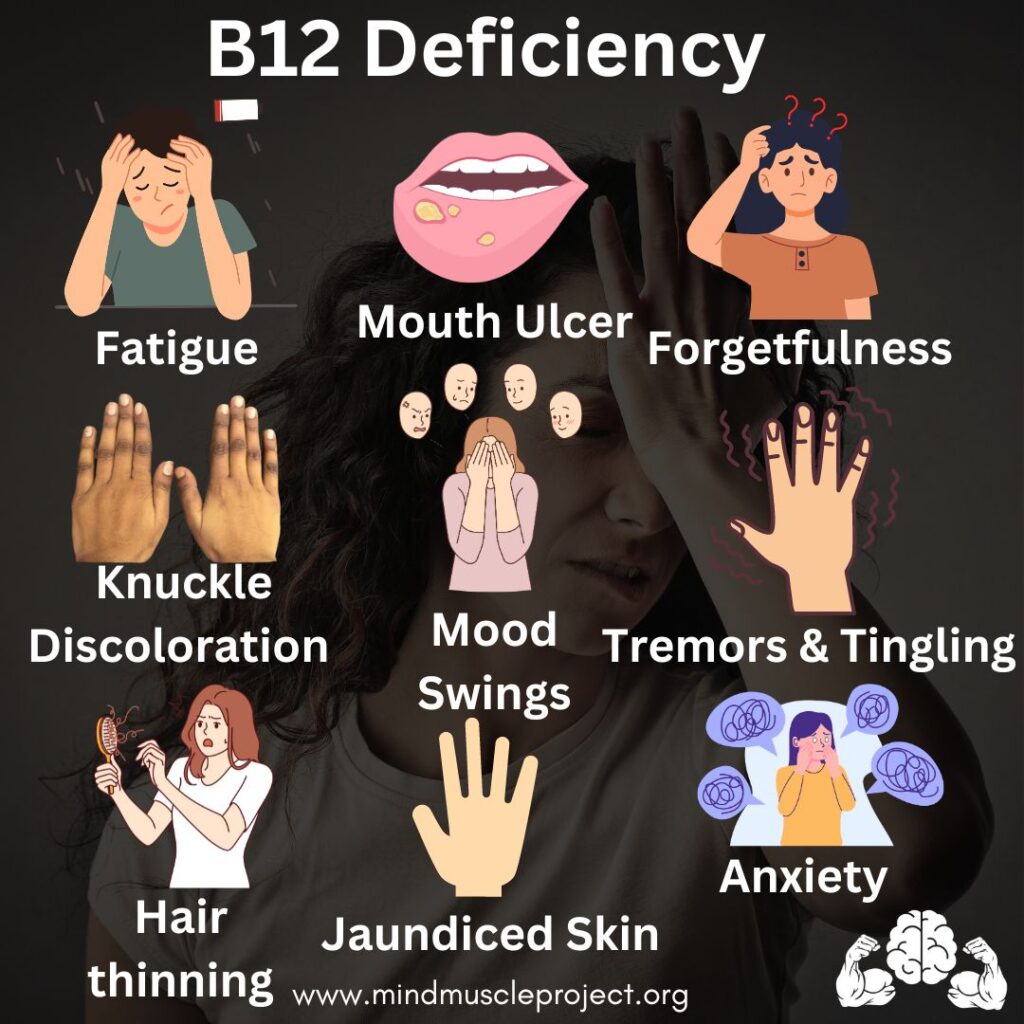
Signs and Symptoms of B12 Deficiency #
Vitamin B12 deficiency can show up in various ways:
❌ Fatigue and weakness
❌ Brain fog or decreased cognitive function
❌ Tingling or numbness (nerve damage)
❌ Pale or yellowish skin
❌ Mood changes (irritability, depression)
❌ Vision problems
❌ Shortness of breath
If left untreated, prolonged B12 deficiency can lead to:
- Permanent nerve damage
- Memory loss
- Increased risk of cardiovascular diseases
How to Fix Vitamin B12 Deficiency #
To improve your B12 levels, you need to address both intake and absorption:
1. Include B12-Rich Foods in Your Diet #
Animal-based foods are the only natural sources of B12. Focus on:
- Red Meat 🥩
- Poultry (Chicken) 🍗
- Fatty Fish 🐟 (like salmon and tuna)
- Egg Yolks 🥚 (but remember, bioavailability is low)
- Dairy 🧀
Important Tip: Eggs and dairy alone are not sufficient to correct a deficiency. If you are vegetarian or vegan, supplementation is often necessary.
2. Consider Supplementation #
If you cannot consume B12-rich foods regularly, or have severe deficiency, supplementation becomes essential. Options include:
- Oral B12 supplements (cyanocobalamin or methylcobalamin)
- B12 injections: Often recommended for severe deficiency or poor gut absorption.
Always consult your doctor to determine the appropriate dosage based on your blood test results.
3. Improve B12 Absorption by Fixing Your Gut #
If your gut cannot absorb B12 effectively, dietary intake alone will not resolve the deficiency.
✅ Key steps to improve gut health:
- Reduce antacid and PPI use: Overuse of these medications reduces stomach acid, impairing B12 absorption.
- Address underlying gut issues like low stomach acid, H. pylori infections, or inflammation.
- Focus on gut-healing foods: Bone broth, fermented foods (like yogurt or kimchi), and prebiotic-rich vegetables.
Get Your B12 Levels Tested #
If you suspect B12 deficiency, ask your doctor for a Vitamin B12 blood test. Early detection is critical to prevent long-term complications.
Takeaway: Don’t Ignore B12 Deficiency #
Vitamin B12 is essential for energy, brain health, and overall well-being. Its deficiency is widespread but preventable with the right steps:
✅ Include B12-rich foods like meat, fish, and poultry in your diet.
✅ If dietary intake is inadequate, consider supplements or injections.
✅ Address gut health to improve B12 absorption.
✅ Get tested regularly, especially if you experience symptoms like fatigue, brain fog, or nerve issues.
Remember: Long-term B12 deficiency can have serious and irreversible consequences, so don’t ignore the warning signs. Take action today to safeguard your health!