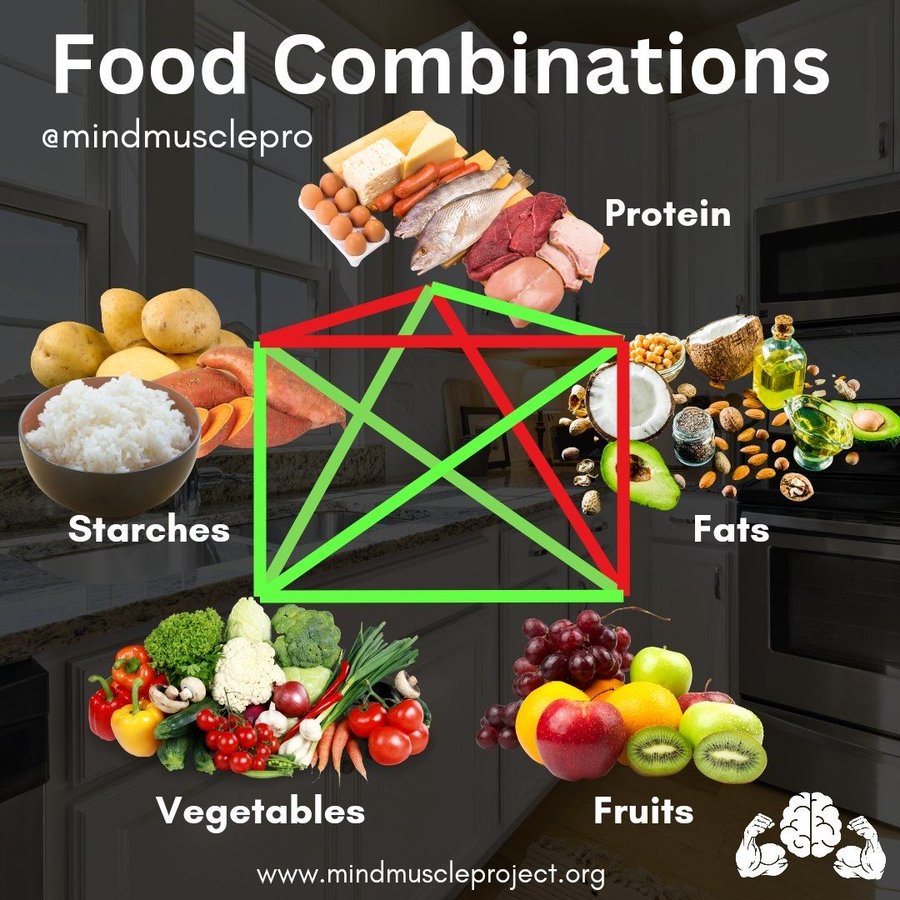
The way we combine foods in a meal has a profound effect on digestion, energy levels, blood sugar, and overall health. Certain food combinations can enhance nutrient absorption, stabilize blood sugar, and even reduce inflammation, while others may slow digestion or spike glucose levels.
Here’s a detailed guide to the most common food combinations, their effects on your body, and how to make the most of each pairing.
1. Protein + Fats #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ High Satiety: Keeps you feeling full for longer.
- ☑️ Stabilizes Blood Sugar: Prevents rapid sugar spikes and crashes.
- ☑️ Supports Hormone Production: Healthy fats aid in synthesizing hormones.
Example: Steak + Avocado #
This pairing delivers protein for muscle repair and healthy fats to support long-term energy and satiety.
2. Protein + Vegetables #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Anti-inflammatory: Combats chronic inflammation with antioxidants.
- ☑️ Supports Gut Health: High fiber content promotes a healthy microbiome.
- ☑️ Promotes Detoxification: Vegetables contain compounds that support liver function.
Example: Grilled Fish + Broccoli #
A nutrient-dense combo that aids digestion and reduces inflammation, perfect for a balanced meal.
3. Protein + Starches #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Moderates Blood Sugar Spikes: Protein slows carbohydrate absorption.
- ☑️ Provides Sustained Energy: Great for active individuals needing prolonged energy.
Potential Drawbacks: #
- ❌ Slows Digestion: Overconsumption can lead to bloating.
- ❌ Not Ideal for Metabolic Health: Refined starches can trigger insulin spikes.
Example: Chicken + White Rice #
This combination fuels your body with energy but should be consumed mindfully to avoid overloading on carbs.
4. Protein + Fruits #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Quick Energy Boost: Combines protein with natural sugars for immediate energy.
- ☑️ Aids Muscle Recovery: Fruits like pineapple contain enzymes that support protein digestion.
Potential Drawbacks: #
- ❌ Digestive Discomfort: Protein and fruit digest at different speeds.
- ❌ Not Ideal for Insulin Resistance: May elevate blood sugar levels in sensitive individuals.
Example: Chicken + Pineapple #
This pairing works well post-workout but should be avoided by those with metabolic concerns.
5. Fats + Vegetables #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Enhances Vitamin Absorption: Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) are better absorbed.
- ☑️ Reduces Inflammation: Healthy fats like olive oil combat inflammation.
- ☑️ Boosts Antioxidant Bioavailability: Fats improve the absorption of antioxidants in vegetables.
Example: Olive Oil + Spinach #
A nutrient-packed combination that boosts bioavailability and supports overall health.
6. Fats + Starches #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Slows Glucose Absorption: Fats moderate the glycemic response to starches.
- ☑️ Reduces Glycemic Impact: Whole-food starches paired with fats keep blood sugar stable.
Potential Drawbacks: #
- ❌ High Calorie Combination: Can promote fat storage when overconsumed.
- ❌ Increases Inflammation: Refined starches paired with fats can trigger inflammation.
Example: Sweet Potato + Ghee #
A comforting and satiating option, but portion control is key to avoid overloading on calories.
7. Fats + Fruits #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Slows Sugar Absorption: Helps prevent blood sugar spikes from fruit.
- ☑️ Stabilizes Blood Sugar: Especially effective with low-glycemic fruits like berries.
Potential Drawbacks: #
- ❌ Insulin Spikes: Overconsumption, especially with high-sugar fruits, can still elevate blood sugar.
Example: Berries + Coconut Cream #
A perfect dessert-like snack that combines fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats.
8. Starches + Vegetables #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Improves Gut Microbiome Health: Fiber from vegetables supports good gut bacteria.
- ☑️ Slows Carbohydrate Absorption: Prevents post-meal blood sugar spikes.
- ☑️ Reduces Glycemic Response: High-fiber veggies balance starch digestion.
Example: Lentils + Veg Salad #
A nutrient-dense, high-fiber combo that’s great for gut health and steady energy.
9. Starches + Fruits #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Combines Fiber & Antioxidants: Good for quick energy needs.
Potential Drawbacks: #
- ❌ High Glycemic Load: Carb-dense choices can cause blood sugar spikes.
- ❌ Not Ideal for Blood Sugar Control: Avoid for those managing insulin resistance.
Example: Oats + Banana #
An energizing breakfast option, but moderation is important to prevent sugar crashes.
10. Vegetables + Fruits #
Benefits: #
- ☑️ Boosts Nutrient Diversity: Combines vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants from both food groups.
- ☑️ Low Glycemic: Works well with fiber-rich fruits like guava or berries.
Example: Cucumber + Guava #
A refreshing snack that delivers a variety of nutrients while keeping blood sugar stable.
Factors to Consider in Food Combinations #
While these food pairings offer specific benefits, their effects can vary based on individual factors such as:
- Portion Sizes: Overeating can negate the benefits of even the best combinations.
- Metabolism: People with different metabolic rates may respond differently to certain pairings.
- Dietary Context: The overall balance of your diet influences how effective these combinations are.
Final Thoughts #
Food combinations can play a powerful role in your health by optimizing digestion, stabilizing blood sugar, and enhancing nutrient absorption. By understanding how different pairings work, you can design meals that align with your health goals and individual needs.