- What is Hypothyroidism?
- How Does the Thyroid Work?
- Symptoms of Hypothyroidism
- Causes of Hypothyroidism
- Diagnosing Hypothyroidism
- Subclinical Hypothyroidism
- Nutrients Essential for Thyroid Health
- Lifestyle Strategies to Support Your Thyroid
- Root Cause vs. Symptom Management
- Takeaway: Supporting Thyroid Health
The thyroid gland is a small yet mighty organ that plays a pivotal role in your overall health. This butterfly-shaped gland located in your neck regulates crucial functions like metabolism, body temperature, and energy levels. When the thyroid gland doesn’t function properly, it can lead to disorders such as hypothyroidism, where the thyroid produces insufficient hormones.
In this post, we’ll explore the essential role of the thyroid gland, the causes and symptoms of hypothyroidism, how it’s diagnosed, and actionable steps to support thyroid health.
What is Hypothyroidism? #
Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland fails to produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to a slowdown in metabolic processes. This condition can affect multiple systems in the body and often goes undiagnosed for years due to its subtle symptoms.
How Does the Thyroid Work? #
The thyroid gland releases hormones in response to a signal from the pituitary gland called TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone). These hormones are responsible for regulating metabolism and energy levels. The two primary hormones produced by the thyroid are:
- T4 (Thyroxine): A prohormone that must convert into T3 to become active.
- T3 (Triiodothyronine): The active hormone that regulates vital bodily functions.
Key Facts About Thyroid Hormones: #
- The thyroid produces 80-90% T4 and 10-20% T3.
- T4 converts into T3 in the thyroid, liver, kidneys, and other tissues as needed.
- Excess T4 that is not converted to T3 becomes Reverse T3 (RT3), an inactive form cleared by the body.
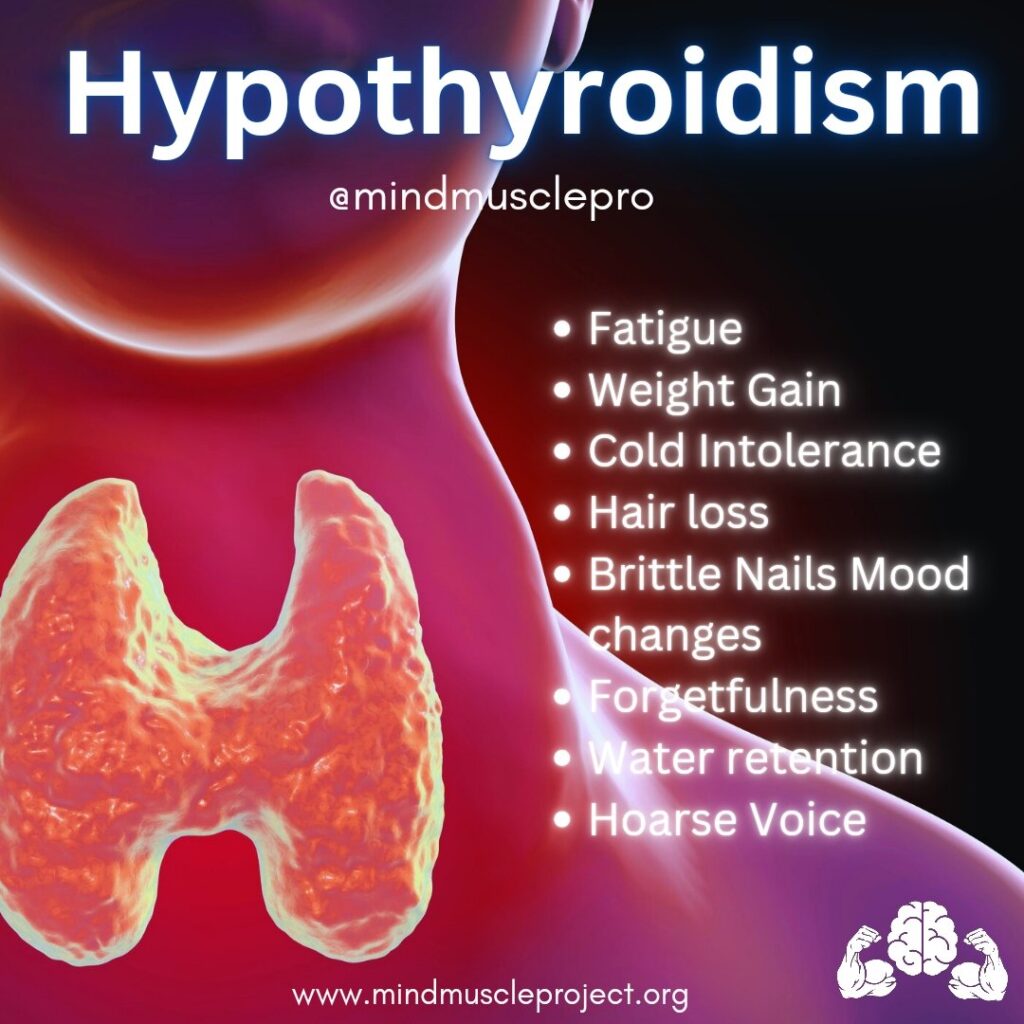
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism #
Hypothyroidism often develops slowly, and its symptoms can be mistaken for other conditions. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and sluggishness
- Weight gain
- Hair thinning or hair loss
- Dry skin
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Depression or brain fog
- Slow heart rate
Causes of Hypothyroidism #
Several factors can lead to hypothyroidism, including:
- Autoimmune Conditions:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis is a common autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland.
- Poor T4 to T3 Conversion:
- The thyroid may produce enough T4, but the body struggles to convert it into active T3.
- Nutrient Deficiencies:
- Selenium, iodine, and zinc are essential for thyroid hormone production and conversion.
- Chronic Stress and Inflammation:
- These disrupt the delicate balance of thyroid hormone production.
- Liver or Kidney Dysfunction:
- These organs play a significant role in converting T4 into T3.
- Environmental Toxins:
- Heavy metals like mercury can harm thyroid function.
Diagnosing Hypothyroidism #
Accurate diagnosis is crucial to understanding the nature of thyroid dysfunction. The most effective tests include:
- Free T3: Measures active thyroid hormone levels.
- Free T4: Measures inactive thyroid hormone levels.
- TSH: Indicates how much the pituitary gland is signaling the thyroid.
- Anti-TPO (Thyroid Peroxidase Antibodies): Detects autoimmune activity.
- Anti-Tg (Thyroglobulin Antibodies): Identifies immune responses specific to the thyroid.
Why TSH Alone Isn’t Enough #
While TSH levels provide insight into the strength of the signal sent to the thyroid, they don’t reveal whether the thyroid is responding appropriately or if T4 is converting into T3 effectively.
Subclinical Hypothyroidism #
This is a milder form of hypothyroidism where thyroid hormone levels are slightly reduced, but not enough to classify as full-blown hypothyroidism. Symptoms may be subtle and can often be managed through dietary and lifestyle changes.
Nutrients Essential for Thyroid Health #
Ensuring your diet includes these nutrients can help support optimal thyroid function:
- Selenium: Found in Brazil nuts, eggs, and fish, selenium supports T4 to T3 conversion.
- Iodine: Found in iodized salt, seaweed, and seafood, iodine is critical for hormone production.
- Zinc: Found in shellfish, seeds, and legumes, zinc aids thyroid hormone synthesis.
- Vitamins B2, B6, C, and E: These vitamins help regulate and optimize thyroid function.
Lifestyle Strategies to Support Your Thyroid #
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Focus on nutrient-dense foods, especially those rich in selenium, iodine, and zinc.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can interfere with thyroid function. Incorporate relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
- Reduce Toxin Exposure: Avoid heavy metals and endocrine disruptors found in plastics and processed foods.
- Support Gut Health: A healthy gut improves nutrient absorption and reduces inflammation, both critical for thyroid health.
- Avoid Extremely Low-Calorie Diets: These can suppress thyroid hormone production and slow metabolism.
Root Cause vs. Symptom Management #
Doctors often treat hypothyroidism with Thyroxine (T4) supplementation, which helps restore hormone levels. While this can address symptoms, it doesn’t always tackle the root cause, such as autoimmune conditions or poor T4 to T3 conversion. Identifying and addressing the underlying issues is key to long-term thyroid health.
Takeaway: Supporting Thyroid Health #
The thyroid gland is a cornerstone of your body’s overall health. Hypothyroidism can disrupt critical functions, but with proper diagnosis, targeted nutrients, and lifestyle strategies, it’s possible to restore balance and improve thyroid function.
Key Steps to Take: #
- Get a comprehensive thyroid panel, including Free T3, Free T4, TSH, Anti-TPO, and Anti-Tg.
- Address nutrient deficiencies with foods rich in selenium, iodine, and zinc.
- Manage stress and inflammation to support thyroid hormone production.
- Consult with a healthcare professional to address the root cause of your thyroid dysfunction.
By taking a proactive approach, you can better manage hypothyroidism and support your thyroid for optimal health.