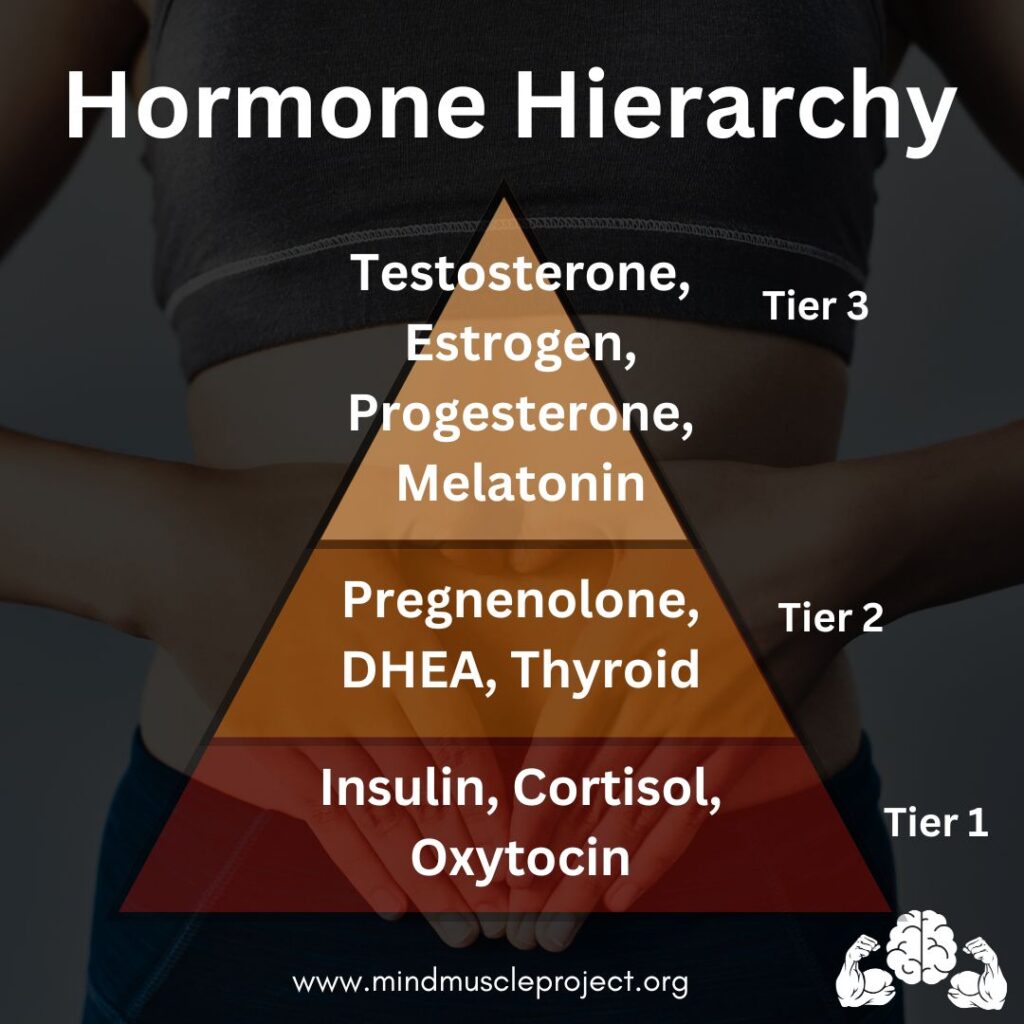
Hormones are the unsung heroes of our body, intricately connected in a hierarchy that impacts everything from your mood and energy to your metabolic health. These biochemical messengers don’t work in isolation—they influence and depend on one another to keep your body running smoothly.
To better understand this intricate system, hormones can be classified into three tiers based on their functions and interdependencies: Foundation (Tier 1), Precursors (Tier 2), and Optimizers (Tier 3). Let’s dive into each tier, why it matters, and how you can support your hormonal health.
The 3-Tier Hormonal Hierarchy #
Tier 1: The Foundation Hormones #
These are the cornerstone of hormonal health. They form the foundation of the entire hierarchy and directly influence your overall stability. Imbalances in these hormones can ripple through the body, disrupting other hormonal functions.
Key Hormones in Tier 1: #
- Insulin
- Role: Regulates blood sugar levels and energy storage.
- Importance: Stable insulin levels prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes, reducing the risk of insulin resistance and diabetes.
- Cortisol
- Role: Known as the stress hormone, it controls energy availability, inflammation, and metabolism.
- Importance: Chronic stress and high cortisol can lead to inflammation, poor energy levels, and disrupted sleep.
- Oxytocin
- Role: Often referred to as the “connection hormone,” it is critical for emotional well-being and stress regulation.
- Importance: Oxytocin fosters feelings of trust, bonding, and emotional stability.
Focus Areas for Tier 1 Stability:
- Blood sugar control: Maintain a balanced diet and avoid excessive refined carbs.
- Stress management: Practice mindfulness, yoga, or meditation to reduce cortisol spikes.
- Building meaningful connections: Cultivate relationships that boost oxytocin levels.
Tier 2: The Precursor Hormones #
Once Tier 1 hormones are stable, Tier 2 hormones come into play. These are “precursor hormones,” meaning they serve as building blocks for other hormones, including sex and stress-related hormones.
Key Hormones in Tier 2: #
- Pregnenolone
- Role: Known as the “mother hormone,” it’s derived from cholesterol and serves as the precursor to cortisol, DHEA, and sex hormones.
- Importance: Adequate pregnenolone ensures your body can produce downstream hormones like estrogen and testosterone.
- DHEA (Dehydroepiandrosterone)
- Role: Supports energy, immune function, and the production of testosterone and estrogen.
- Importance: DHEA declines with age, which can affect vitality and hormonal balance.
- Thyroid Hormones
- Role: Regulate metabolism, energy production, and cellular repair.
- Importance: A sluggish thyroid can lead to weight gain, fatigue, and impaired metabolic health.
Focus Areas for Tier 2 Stability:
- Healthy fat intake: Consume cholesterol-rich foods like eggs, fatty fish, and nuts to support hormone synthesis.
- Stress reduction: Chronic stress can deplete pregnenolone, leading to hormone imbalances.
- Adrenal health: Support your adrenal glands with adaptogens like ashwagandha or rhodiola.
Tier 3: The Optimizer Hormones #
At the top of the hierarchy are the hormones that enhance and optimize overall health. While not foundational, they play a critical role in muscle health, reproductive functions, and emotional well-being.
Key Hormones in Tier 3: #
- Testosterone
- Role: Enhances muscle strength, libido, and overall vitality.
- Importance: Both men and women need testosterone for energy, motivation, and metabolic health.
- Estrogen
- Role: Regulates reproductive health, mood, and bone density.
- Importance: Balanced estrogen is crucial for menstrual health, mood stability, and preventing osteoporosis.
- Progesterone
- Role: Balances estrogen levels and promotes hormonal stability.
- Importance: Adequate progesterone supports fertility, a calm mood, and restful sleep.
Focus Areas for Tier 3 Stability:
- Sleep optimization: Deep, restorative sleep is essential for balancing testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone levels.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can deplete Tier 3 hormones, especially testosterone and progesterone.
- Consistent lifestyle practices: Include resistance training and nutrient-rich foods to support hormone optimization.
How to Apply the Hormonal Hierarchy in Daily Life #
The hormone hierarchy provides a framework to approach your health step by step:
- Start with Tier 1: Focus on stabilizing your blood sugar, managing stress, and fostering meaningful relationships.
- Support Tier 2: Incorporate healthy fats, manage adrenal health, and optimize thyroid function.
- Enhance Tier 3: Build a lifestyle around quality sleep, stress reduction, and consistent exercise.
Final Thoughts #
Understanding the hormonal hierarchy is key to achieving optimal health. By focusing on the foundational hormones first and working your way up, you can ensure your body operates at its best. Remember, hormonal health is not about quick fixes—it’s about creating sustainable habits that support your body’s natural processes.